Mean Reversion Definition
Reversion to the mean, or "mean reversion," is just another way of describing a move in stock prices back to an average. This could be a moving average, a volume-weighted average price (vwap), or any other average, like a value line within a channel, for example. Often a mean reversion will occur when asset prices become extended in either direction.
Mean reversion trading can be a very profitable trading strategy when employed with other technical indicators, chart patterns, or candlestick patterns. When a confluence of confirming chart patterns occurs, mean reversion trades can often signal reversals and lead to short-term pullbacks in trends.

How to create a mean reversion trading strategy?
The best way to create a mean reversion trading strategy is to study trending stocks. When a stock trends, it tends to put in a series of higher highs and higher lows, or lower highs and lower lows, depending on the context. Astute traders who study the charts of these stocks can often find inflection points where the price becomes oversold or overbought.
When a stock enters this over-extended territory, it can become a ripe candidate for a reversal back to the mean (average). In other to create a mean reversion trading strategy, you'll need a few things:
- 100s of charts annotated with examples of stocks that revert to the mean
- Definable characteristics that show optimal entry points for the mean reversion trade
- Multiple confirming signals like a reversal candlestick pattern, sign of exhaustion, trend overthrow, or other indicator
- The "mean" or average in which the stock or asset could return to as a target
We've written an entire post on how to trade trends, so be sure to check that out in addition to the information below.
Which moving average is best for mean reversion?
Usually, the 10sma, the 20ema, and the 50sma are the best moving averages for mean reversion. However, in order to create a mean reversion trade using moving averages, you'll need to experiment with some of the more popular simple moving averages and exponential moving averages. Different timeframe charts often have different moving averages that work better than other time frames. So, be sure to play around with as many as you can until you find the right fit.
In this example, we'll be using the 10sma, the 20ema, the 50sma, or the 200sma. In our trading, we've found that these often provide a good indication of the shorter, intermediate, and longer-term trend. As such, these moving averages will often come into play as a stock rises and falls along its upward path. In other words, these often represent the best targets for mean reversion trades.
Mean reversion trade with moving averages example
In this example of GOOGL, we have a solid up-trending environment. The macro context is a strong bull market. When in a strong bull market, you obviously want to be looking for opportunities to go long, as that is where the easy money is.
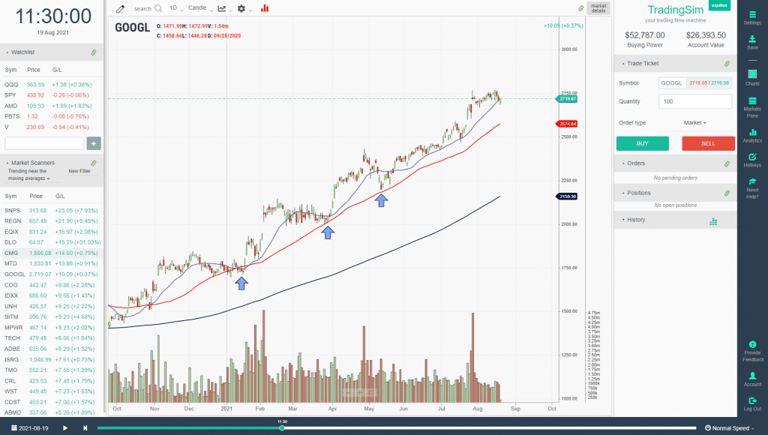
In this example, we have the 20ema in blue, the 50sma in red, and the 200sma in black. For a moment, just visualize all three of these on the chart and their relation to each other. Notice that as the 20ema becomes extended from the 50sma, it often signals a pullback to the 50sma as "check in".
In a healthy trend, you will likely see a stair-step upwards until the move reaches a climactic pitch, signaling the end of the trend. For this mean reversion trading strategy, the entry criteria are quite simple. As you can see from the blue arrows, you look for a confirmation of support along the 50sma, then go long on the pocket pivot with increased volume as price moves back through the shorter-term moving averages.
Mean reversion trading with channels
If moving averages aren't your thing, channels can be a great way to judge the support and resistance of any trend, vertical or horizontal. Not only can it help visualize where support is coming in at the lows, but also where resistance is being met at the highs.
The best way to draw channels for mean reversion is to connect two points on either side of the new trend formation, the top or the bottom. Once you've drawn your line, clone the line on the other side of the developing channel. The more channels you study, the better you'll get at judging the support and resistance sooner in the trend.
With your channel lines drawn, it becomes an anticipatory trade idea to find the regression to the mean of the channel -- that is, to either side of the channel or to the value line in the middle of the channel.
Mean reversion trading channels example
Let's take the Google chart that we used above, but repurpose it with channels instead of moving averages, this time. Pay close attention to the way in which GOOGL overthrows the upper bounds of the channel ever-so-often. This is an important observation.
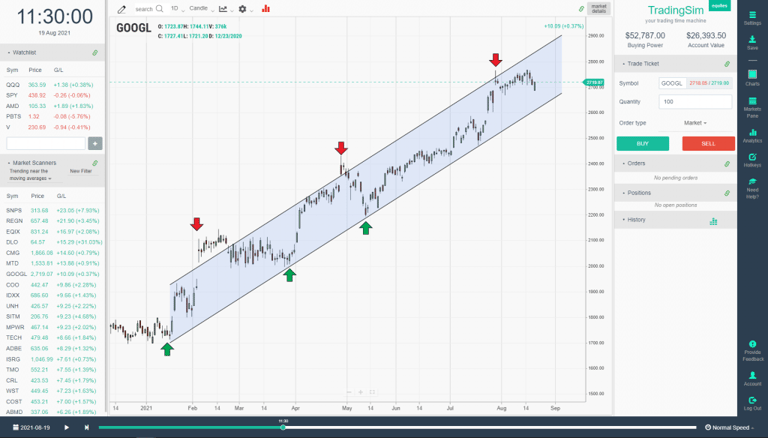
An overthrow of a channel signals an acceleration of price movement. You'll want to pay close attention to these events because they often signal reversals. They can be a lot like springs and upthrusts in horizontal channels. When the price acceleration fails back into the channel, it provides a good entry signal with a definable risk area just above or below the overthrow price area.
If you are long, it can be a great way to judge when to sell some of your profits into climactic price action. Then, as you can see from the green arrows in the channel above, the support area provides a great risk/reward area to add back to your positions. We call this "campaigning" a stock. Paying yourself along the way, then adding back into support areas.

Mean reversion trading in down trending stocks
The mean reversion trade for down trending stocks really looks no different, just a mirror image of an up trending stock. In this scenario, you're looking for continued weakness in stocks. In other words, rallies should be met with resistance somewhere into the mean reversion of the channel.
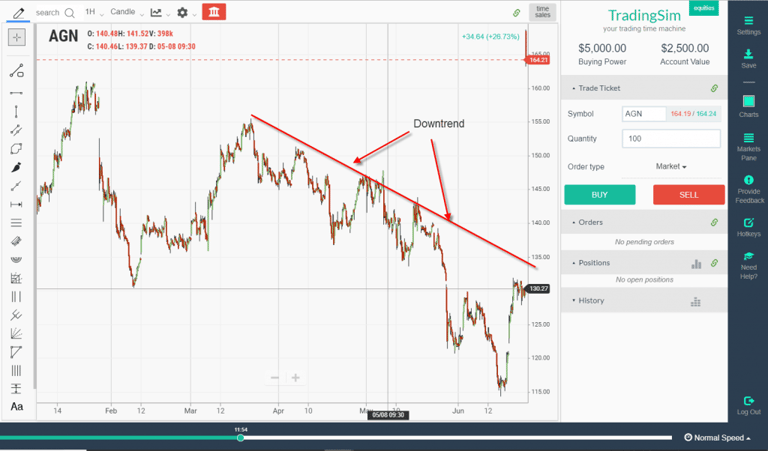
As the asset approaches the mean, it's your goal to determine the strength of the pullback and the broader context of the stock or stock market. Either way, these areas of resistance often provide very good risk to reward for short-sell trades.
One thing you should notice in the image above, however, is that eventually, the stock becomes EXTREMELY oversold. Notice how it breaks the lows of the channels also, entering a free-fall. This is another opportunity to capitalize on a mean reversion trade called a parabolic reversal strategy.
Mean reversion in parabolic stocks
When a stock goes parabolic, it often becomes the target of many traders looking to take advantage of the mean reversion trade. While stocks can continue their upward or downward momentum much further than many traders would suspect, they can't go up or down forever. Eventually, supply or demand will reverse the course.
But, how do you time this properly? First, let's examine the difference between a parabolic stock and a healthily trending stock in these two images:
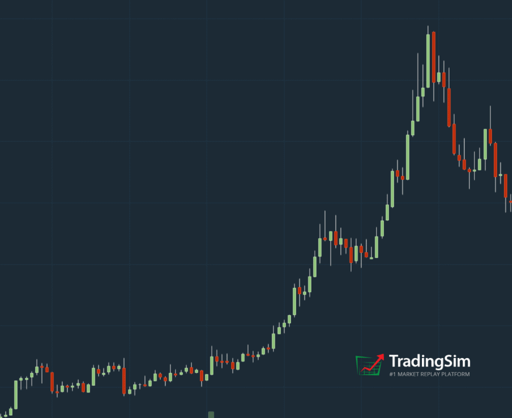
Notice how the first image in white background is following a steady trend upward. The second image in the black background is going parabolic. What differentiates the two? Essentially, the slope of the incline. In parabolic stocks, FOMO is often reaching a fever pitch that is unsustainable.
The higher it goes, the harder it is likely to fall. But to take advantage of the mean reversion trade, you need to look for a few things: a bearish candlestick pattern and a potential resistance area on a longer-term time frame. If the latter doesn't exist, you'll simply have to use your own judgment with multiple time frame charts or moving average extensions.
Mean reversion in parabolic stocks example
Let's dial into the parabolic stock above and analyze how you could have used a bearish engulfing candle to time your entry into the trend acceleration. This stock was $EYES:
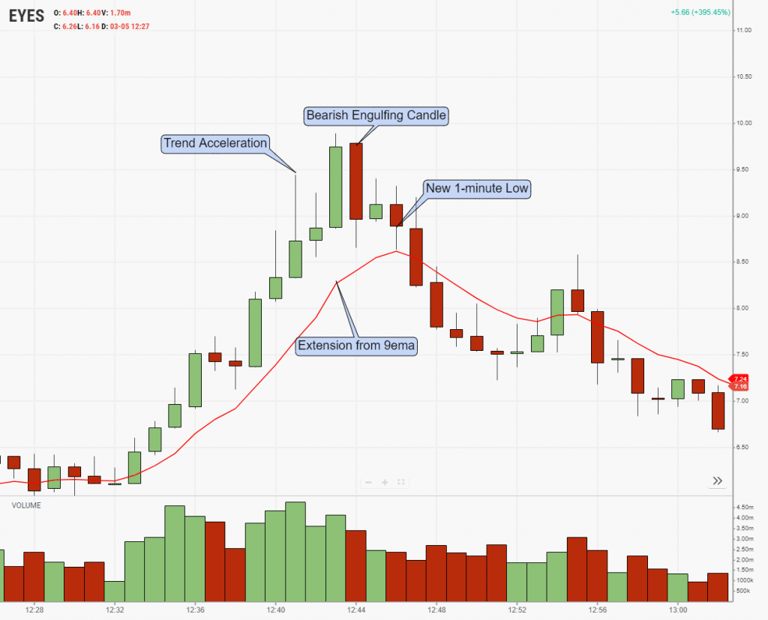
As the trend accelerates, you notice that the stock becomes extended from the 9-ema on a 1-minute chart. It then overcomes and squeezes the first two hammer candles. It then produces a large red bearish engulfing candle that stops the upward momentum, leading to two lower highs on the backside of this trade.
Let's look at what would confirm this trade for us:
- Overextension on multiple time-frames like 1-min and 5-min
- Price acceleration
- Volume acceleration
- Extension from moving averages
- Bearish candlestick pattern confirmation
- Lower highs
Altogether, this created a great opportunity to short a stock back to the mean. But where would your target have been?
Finding targets for mean regression trades
One of the best ways to find a target for a mean regression trade is to use not only the moving averages but also VWAP. VWAP is a measure of the volume-weighted average price of a stock on an intraday basis. When you're day trading, it can be a great tool to target a reversion to the mean.
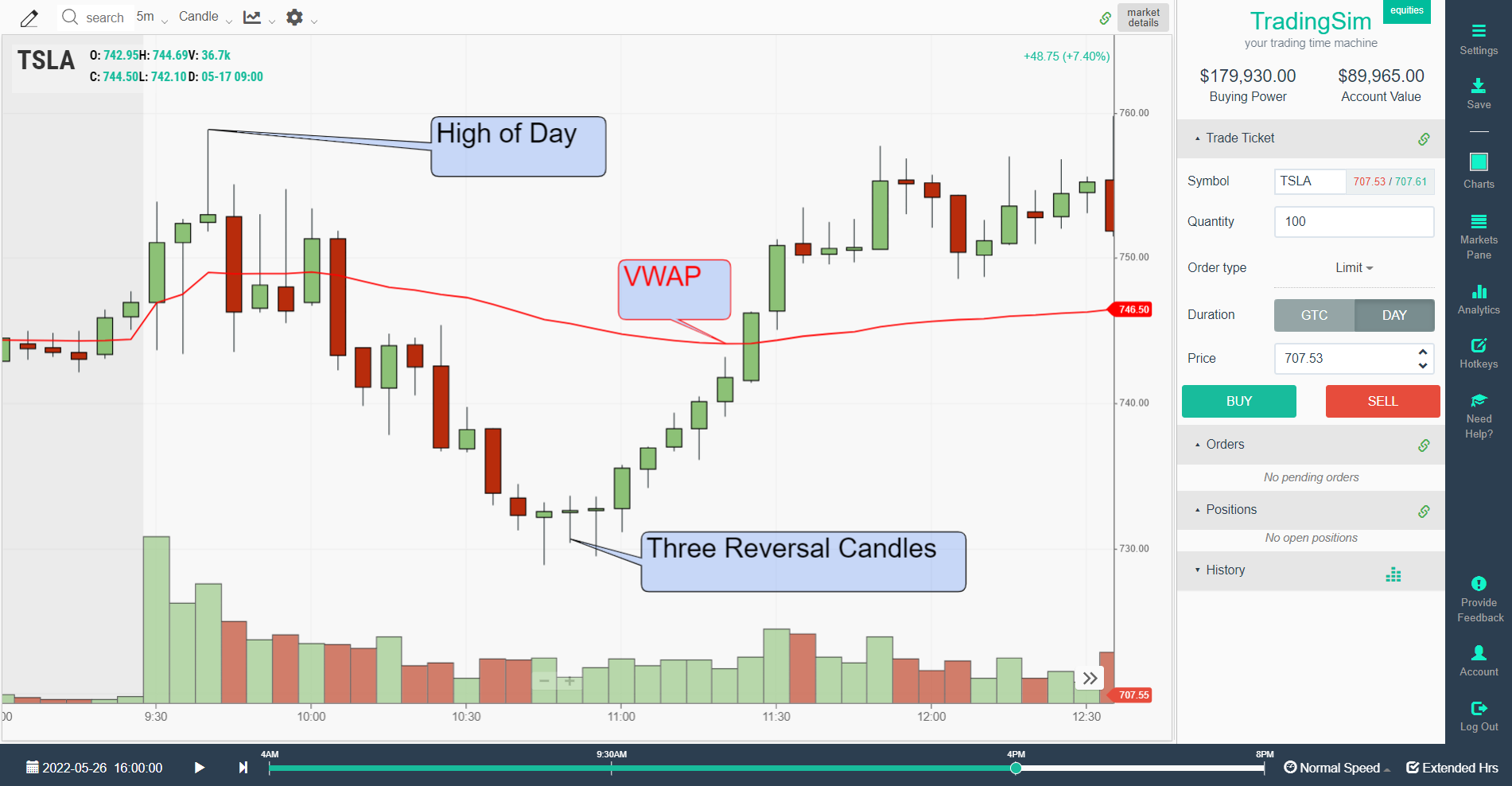
In this example with TSLA, we see a sharp decline that wasn't sustainable in the morning trading session. After confirming 3 bullish reversal candles and a gravestone doji, TSLA marched right back to the VWAP in red.
If executing this trade based on the concept of mean reversion, you have two targets here. The first target is the VWAP line. Then, using trade management techniques, you could have held for higher prices by putting a stop below the candle that broke vwap. As the price moves higher, you simply move your stop to below each candle producing a new high.
Had you employed this trade management rule, you could have taken half your profits at vwap, then held for a push to the high of day as target 2. You would not have been stopped out until the $753 area, another $9 above vwap!
How to practice the mean reversion trading strategy?
There is no better way to practice the mean reversion trading strategy than in a simulator. Here at TradingSim, we offer an app that allows you to practice mean reversion trades with over three years of historical market data. This allows you to replay the market as though you were live, each day, for three years.
As you study your mean reversion strategy, be sure to take simulated trades and then qualify your stats in our analytics page that is built-in. The more success you have, the more confidence you'll have in trading the mean reversion strategy in a real market environment.


















 Awesome Day Trading Strategies
Awesome Day Trading Strategies 
